The advantage of graphene sheet thermal conductive film
Graphene has excellent thermal properties, and single-layer graphene has a thermal conductivity of up to 5300W/(m∙K). Graphene heat dissipation material represented by graphene thermal film is one of the most promising new heat dissipation materials in the current thermal management field.
Table of Contents
ToggleGraphene sheet thermal conductive film Low Thermal Resistance:Thermal resistance is 40% lower than aluminum and 20% lower than copper
Light weight Material: 25% lighter than aluminum and 75% lighter than copper;
High Thermal conductivity: In-plane thermal conductivity is 5 times higher than that of pure copper
Flexible use: can be made any form of cutting and stitching
Good uniformity: The heat energy can be dif fused from the point heat source to heat dissipation sur face rapidly and the ef fective High temperature resistance:
High Temperature Resistance: 320 °C, low temperature resistance:- 40 °C.
Wide Range of applications: It fits seamlessly on any sur face.
CUSTOM: Film thickness and size can be customized.
Introduction to Thermal Conductive Materials
With the development of electronic devices and products to the field of high integration and high computing, the power dissipation multiplies, and heat dissipation becomes an urgent problem to be solved. Most of the traditional thermal conductive materials are metals (Ag, Cu, Al, etc.), metal oxides (Fe2O3, BeO, Al2O3, etc.), and other non-metallic materials (graphite, carbon black, AlN, etc.).
In the field of heat dissipation of electronic devices and products, traditional heat dissipation materials such as copper and aluminum have been widely used; in recent years, the emergence of graphene materials, with its excellent thermal conductivity, rapid heat dissipation characteristics (convection with the air), as well as lightweight and flexible characteristics, is considered to be a class of highly competitive heat dissipation materials.
Graphene sheet thermal conductive film principle
Graphene has very good thermal conductivity. Pure, defect-free, single-layer graphene has a thermal conductivity of up to 5300 W/mK, by far the highest thermal conductivity of any carbon material, higher than that of single-walled carbon nanotubes (3500 W/mK) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (3000 W/mK). When it is used as a carrier, the thermal conductivity is also up to 1200 W/mK. in addition, the ballistic thermal conductivity of graphene can shift the lower limit of the ballistic thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes per unit circumference and length down.
In thermodynamics, the heat dissipation of graphene heat sink film includes Conduction, Convection and Radiation in several ways, as shown in Figure 1. Specifically for example, the CPU heatsink base and CPU direct contact with the way to take away heat belongs to the heat conduction; common cooling fan driven gas flow that is thermal convection; thermal radiation refers to rely on the ray radiation to transfer heat. In general (below 400 degrees Celsius), the heat sink system mainly relies on thermal conduction and thermal convection, where thermal conduction is mainly related to the thermal conductivity and heat capacity of the heat sink material, and thermal convection is mainly related to the heat dissipation area of the heat sink.
Applications of Graphene Sheet Thermal Conductive Film
At present, in the field of thermal conductivity and heat dissipation, the types of graphene heat dissipation materials that have been widely studied include graphene sheet thermal conductive film, graphene thermal conductive polymer composites, graphene based metal composites, graphene heat dissipation coatings and so on.
Thermal conductive film prepared with graphene material, compared with the traditional artificial graphite thermal conductive film, has the advantages of high theoretical thermal conductivity, adjustable film thickness, flexible and bend-resistant, etc. The important thing is that the resources of graphene material are independent and controllable, and it has become one of the popular materials in the current thermal conductive materials.
Graphene sheet thermal conductive film as an important component of end product heat dissipation, the main role is to dissipate the heat of components and equipment through its own high thermal performance, to prevent overheating of the equipment caused by reduced efficiency or even equipment damage.
Graphene thermal conductive film with high thermal conductivity, lightweight, flexible and other characteristics, has been in the high-end smart phones, tablet PCs and other consumer electronic products in the field of heat dissipation to achieve large-scale commercialization applications, the future is expected to become a folding screen smart phones, smart wearable devices, and other segments of the mainstream heat dissipation program.
In addition, the aerospace field of lightweight heat dissipation materials, high thermal conductivity and other requirements are very demanding, “aerospace-grade” graphene thermal conductive film has been successfully realized application; the global Internet data traffic continues to grow to drive the demand for ICT equipment, graphene heat dissipation material application potential gradually appeared; chip power density continues to improve, giving rise to high thermal conductivity thermal interface material demand. Thermal interface material demand. Graphene thermal conductive film is gradually expanding to semiconductor packaging, new energy vehicles and other thermal management fields.
Preparation method of Graphene Sheet Thermal Conductive Film
Scaled-up preparation under effective cost control is a prerequisite for new materials to move from the lab to the market, and the industry usually uses high-temperature thermal reduction of graphene oxide film to prepare graphene thermal conductive film.
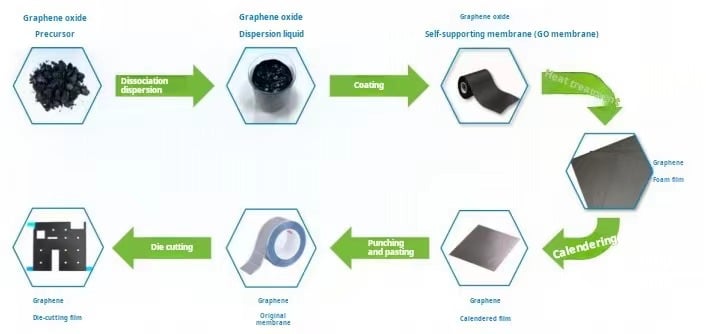
Highly oriented self-assembly of graphene oxide is the core of realizing the high thermal conductivity of graphene film, and graphene oxide microfilms with monolayer rate more than 90% are the key to realize highly oriented self-assembly.
On the one hand, graphene oxide precursor with higher oxidation degree is easier to be dissociated into graphene oxide microfilm with high monolayer rate, which can lead to good dispersion effect and better effect of highly oriented assembly, but it will bring higher oxidation cost.
On the other hand, the graphene oxide slurry with high monolayer rate is prone to agglomeration due to hydrogen bonding, and it is necessary to reduce the solids content in order to achieve uniform dispersion to meet the requirements of the coating process and the realization of the highly oriented assembly, however, the low-solids slurry is not easy to be coated into the ideal thickness of the GO film, which will seriously reduce the coating efficiency, and increase the drying difficulty, which will lead to the manufacturing cost to be increased significantly. Although the solid content of the slurry can be enhanced by adding dispersants or surface treatment agents, it will cause a significant increase in the viscosity of the slurry, making it poorly fluid, resulting in the inability to transport and difficult coating.
Therefore, the good dispersion required by graphene oxide slurry and the high oxidation cost of graphene raw materials, and the high directional assemblage of graphene film and the high process cost in the coating and drying process have become the two main contradictions affecting the economy of scale-up preparation of high-performance graphene film and the major technical obstacles in its industrialization process.